Kubernetes project using labels and selectors and deployments and services
Table of contents
Prerequisites
Assuming that Kubernetes installation processes are done. Let's dive in:-
Commands used for running the Kubernetes practice
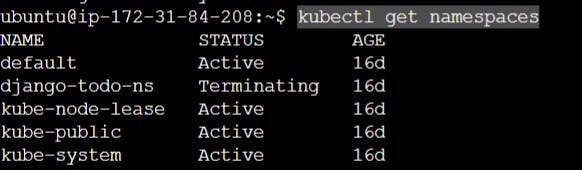
To get the namespaces that are existing.
kubectl get namespaces or kubectl get ns
kubectl get pods -ns=django-todo-ns # To get the pods which are running under the namespace

For creating a namespace
kubectl create namespace django-todo-ns
kubectl get ns

Create a directory for Kubernetes
mkdir deploy_k8s
cd deploy_k8s/
Writing configurations for POD.yml
Please refer to https://kubernetes.io/ always for the latest configurations.
Create pod.yml
vim pod.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: django-todo
namespace: django-todo-ns
spec:
containers:
- name: django-todo
image: ashwathy/django-todo-app:latest //image should be pushed to dockerhub
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Here we need the image to be pushed to the docker hub too.
Now applying it.
kubectl apply -f pod.yml

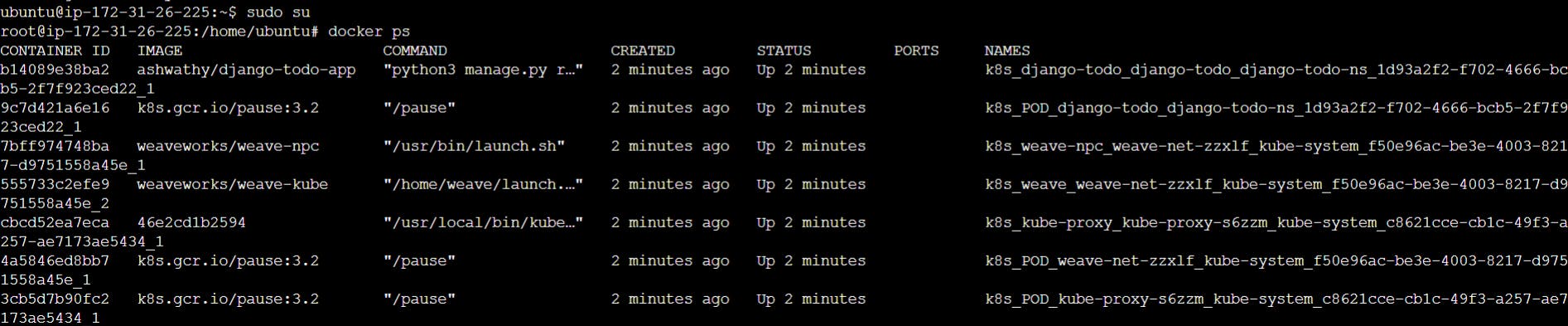
Now go to the worker node
sudo su
docker ps
The pods will be running here.
In case you close the master node use the below command.
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/configonfig
chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/configonfig
export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/.kube/config
In the worker node: The image is running.
sudo su
docker ps
cp pod.yml redit_pod.yml #For reddit clone apps
AutoHealing process:-
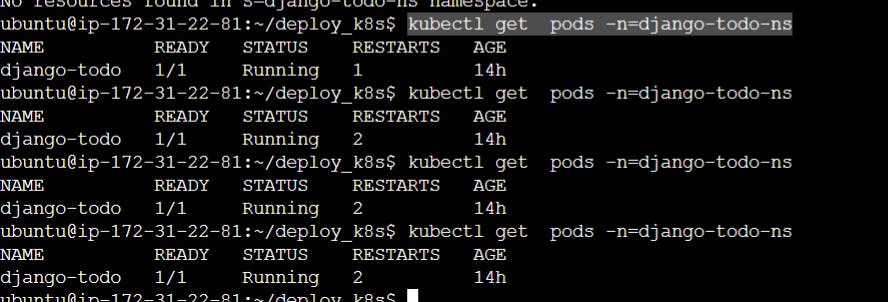
Checking the pods running initially
kubectl get pods -n=django-todo-ns

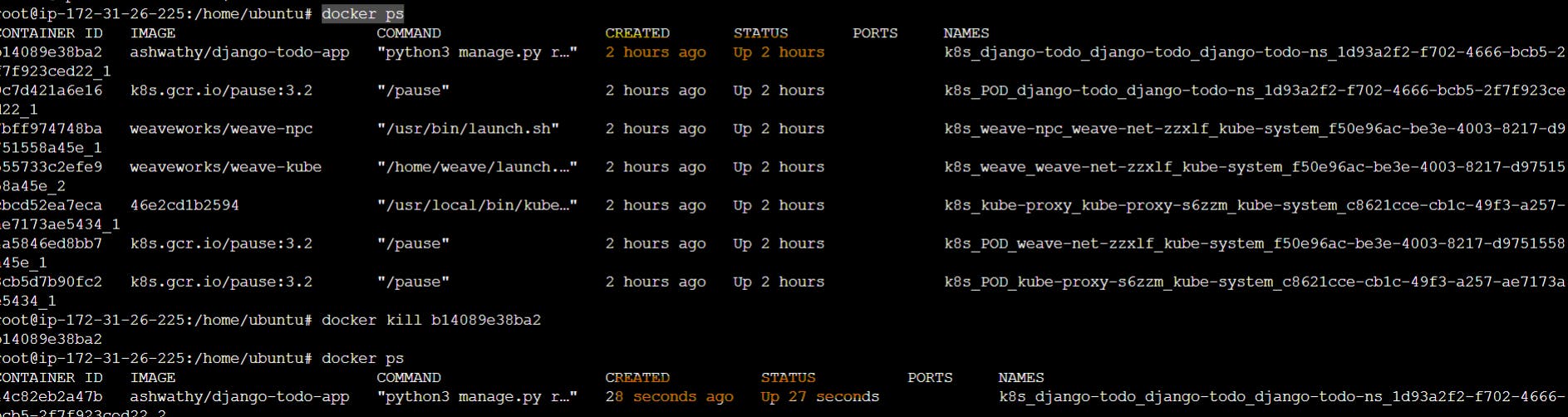
docker ps #In worker node
docker kill <CONTAINERID> #Kill the container and it auto heals
Deleting PODS:-
kubectl delete -f pod.yml #Deleting it in master node
Replica Set/Scaling:-
To get a specific label from the selector we have to create a deployment file:-
vim deployment.yml
YAML fILE
piVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: django-todo-deployment
namespace: django-todo-ns
labels:
app: django-todo
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: django-todo
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: django-todo
spec:
containers:
- name: django-todo
image: trainwithshubham/django:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
Apply the deployment file:-
kubectl apply -f deployment.yml
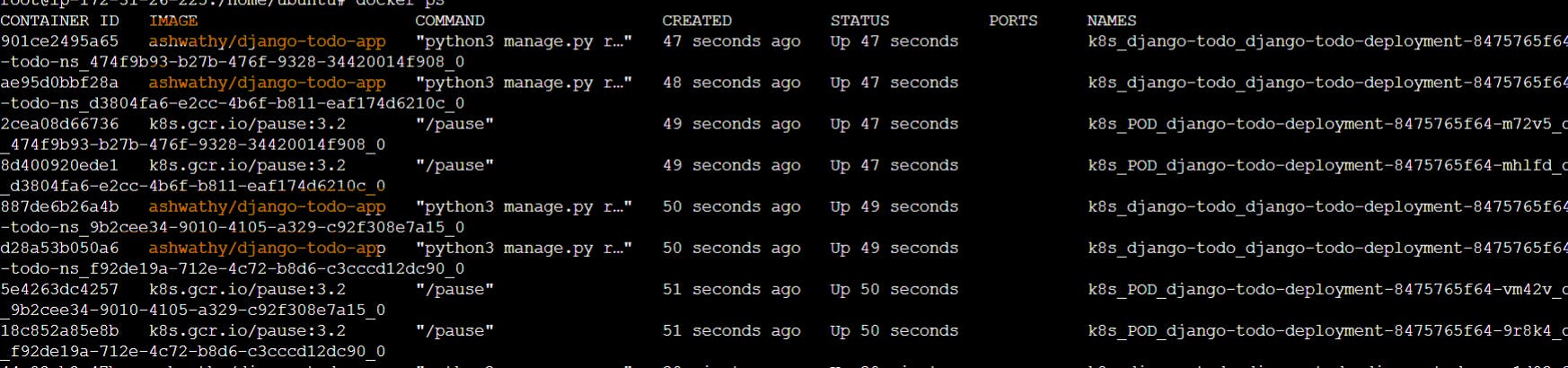
In worker node:- Four containers/pods are running
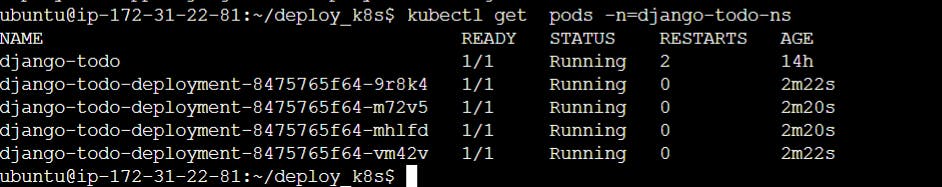
Checking in master node:-
kubectl get pods -n=django-todo-ns or watch kubectl get pods -n=django-todo-ns (It will reresh every 2 seconds)
kubectl get pods -o wide -n django-todo-ns #For a wider view
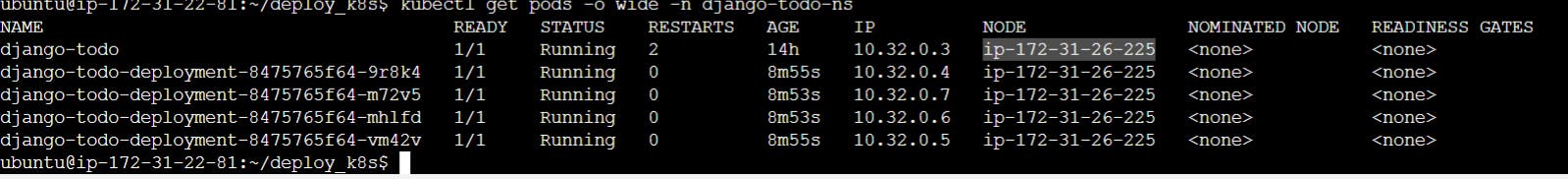
Every pod is having Private IP. For accessing the specific pod we need to go to the specific IP and access the pods which is not possible. So we are interacting with the traffic using the service.yml which gives the label inside the deployment.yml the internet access. Service has 3 types:-
- Give the internal IPs under the labels one port number so that service.yml can connect to it.
2)Cluster IP:- Assign the cluster IP and service.yml can access it.
3)Load Balancer:-According to the load it can access the pods inside the cluster.
Service.yml-
vim service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: django-todo-service
namespace: django-todo-ns
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: django-todo
ports:
# By default and for convenience, the `targetPort` is set to the same value as the `port` field.
- port: 80 // We use the concept of port binding here where 80 will be mapped to 8000 target port and cluster Ip port will be 30007-80 is the host port(-p 80:8000)
targetPort: 8000
# Optional field
# By default and for convenience, the Kubernetes control plane will allocate a port from a range (default: 30000-32767)
nodePort: 30007
Apply the service:-
kubectl apply -f service.yml
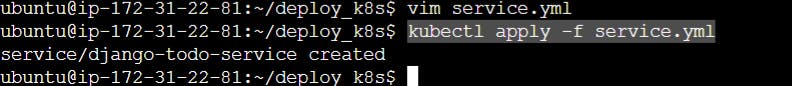
kubectl get service
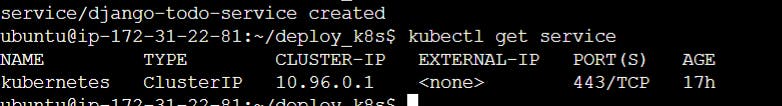
kubectl get service -n django-todo-ns

Apply the service
kubectl apply -f service.yml
Run the port in public ip:3007 and open the port in the worker node
We can change the scaling in replicas and do the deployment command again to scale it. We can use the below command to check all the scaling up and down, Strategy type can also be checked.
kubectl describe deployment.apps/django-todo-deployment -n django-todo-ns